19 Actionable SEO Tips
A comprehensive guide with 19 actionable SEO tips covering keyword research, featured snippets, video optimisation, local SEO, schema markup, and more.

In this guide, I will be providing 19 SEO tips for businesses, webmasters and those wanting to learn more about SEO, as well as offering expert advice from some of the best-known names in the industry.
1. Advanced Keyword Research
Keyword research remains foundational to SEO success. It helps businesses provide search engines with relevant information so users can find them. Since Google’s Hummingbird update, search has shifted toward understanding semantic relevance, meaning comprehensive keyword strategies must consider:
- Semantic keywords
- Long-tail queries
- Question-based queries
- Voice search variations
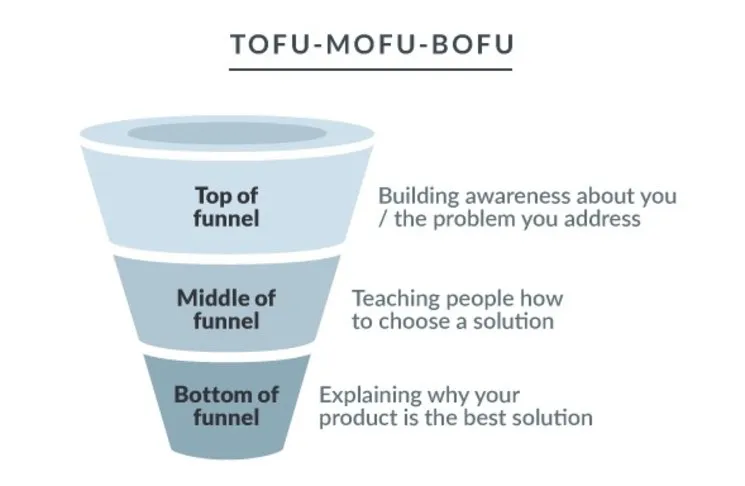
Keyword Categorisation Strategy
A practical approach involves grouping keywords by buyer journey stages:
- Top of the Funnel (TOFU) — Awareness Stage: “Is it possible to repair a broken iPhone screen myself?”
- Middle of the Funnel (MOFU) — Consideration Stage: “Repair a broken iPhone screen”
- Bottom of the Funnel (BOFU) — Ready to Buy Stage: “iPhone screen repair specialist”
Rather than prioritising only high search volume keywords, focus on search intent and appropriate content positioning within the buying cycle.
2. Aim for Featured Snippets Inclusion
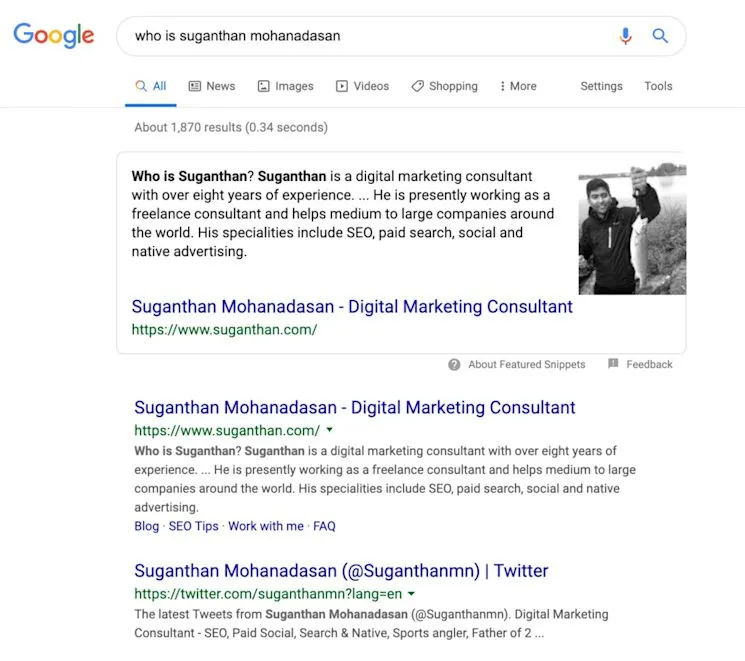
Featured Snippets, known as “position zero,” appear above organic search results, providing direct answers without requiring users to click through results.
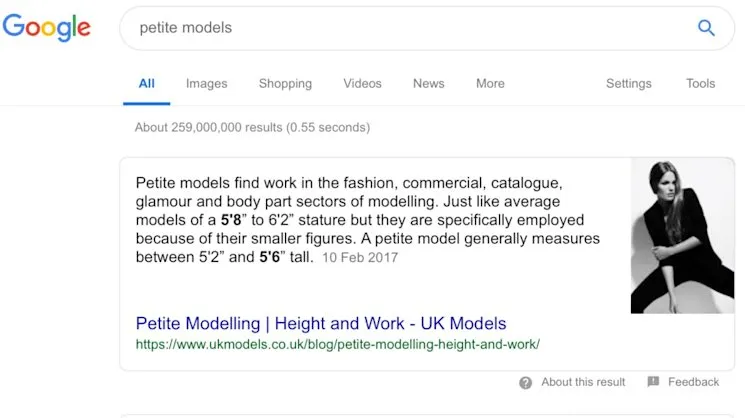
Optimisation requires:
- Original, informative, and concise content
- Clear information presentation in optimal formats
- Reverse-engineering competing snippets
- Proper markup implementation
- Well-formatted tables and ordered lists
- Site authority and responsiveness
- Strong social engagement
3. Try Video Optimisation
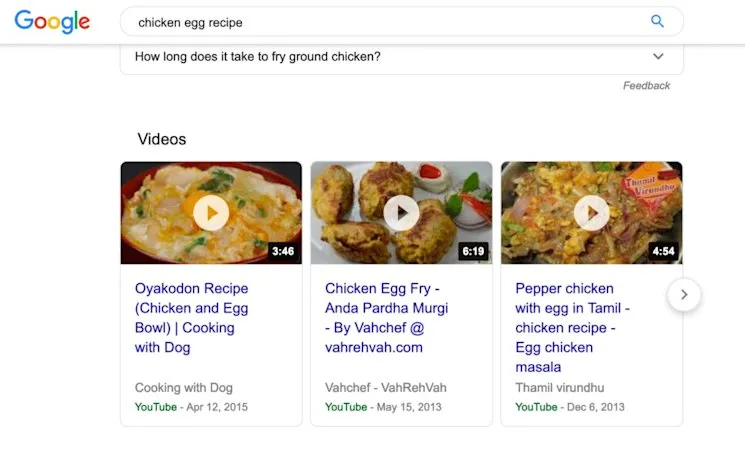
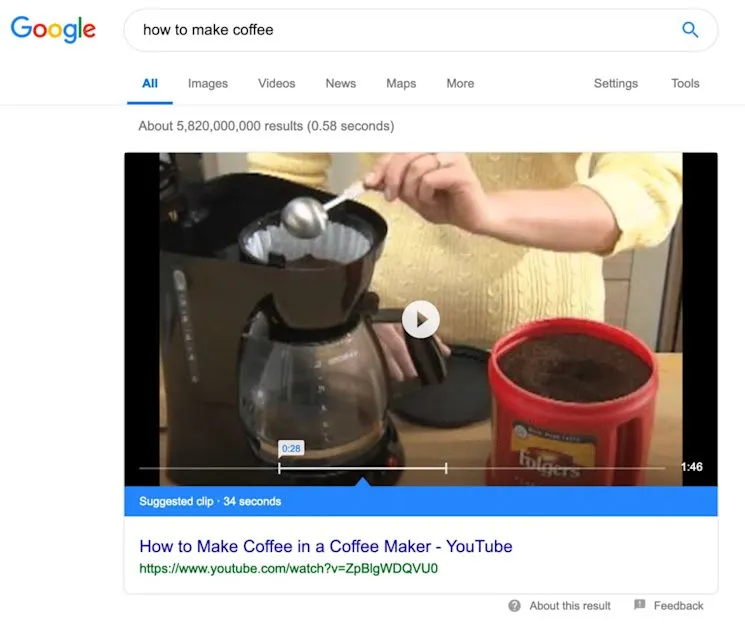
Video content increasingly dominates search results through carousels and featured snippets with video segments.

Key optimisation practices include:
- Creating videos with clear, engaging voice-overs
- Providing accurate transcriptions (manual transcriptions outperform automatic ones)
- Adding timestamps for step-by-step content
- Developing a robust YouTube channel with business-relevant content
- Optimising metadata and descriptions
Important caveat: Video carousel positioning may not benefit e-commerce sites, as it can trap traffic on Google’s properties rather than driving conversions.
4. Better Image Optimisation
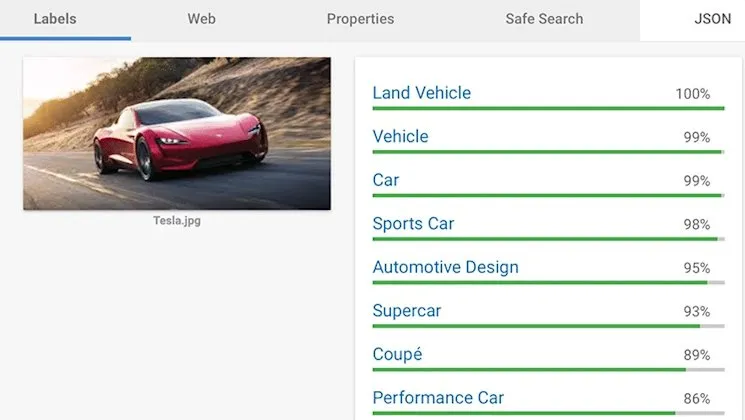
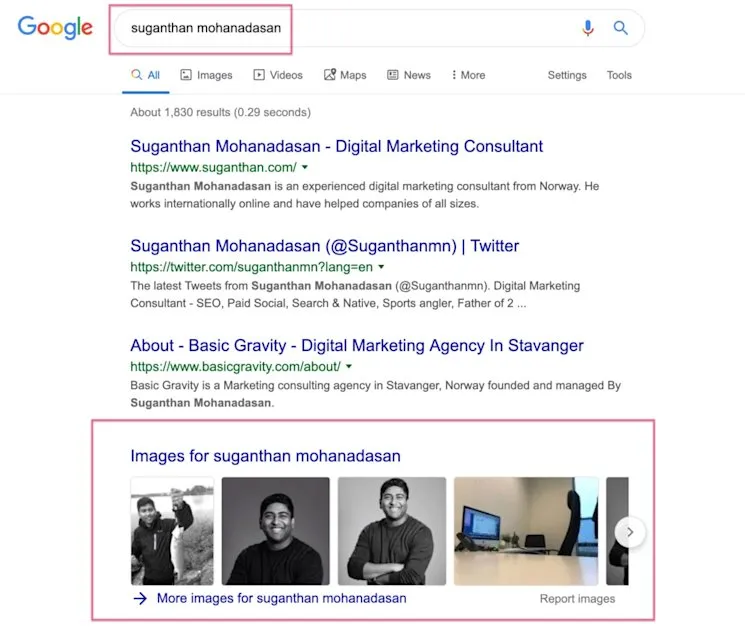
Images remain vital SEO components, though often underutilised. Key image optimisation elements include:
- Provide descriptive alt text
- Include surrounding explanatory text
- Use descriptive filenames and captions
- Implement proper image tags
- Consider next-gen formats (WebP, AVIF) when browser support permits
Google investigates image context, meaning generic images underperform compared to contextually rich alternatives.
5. Don’t Overlook Local SEO
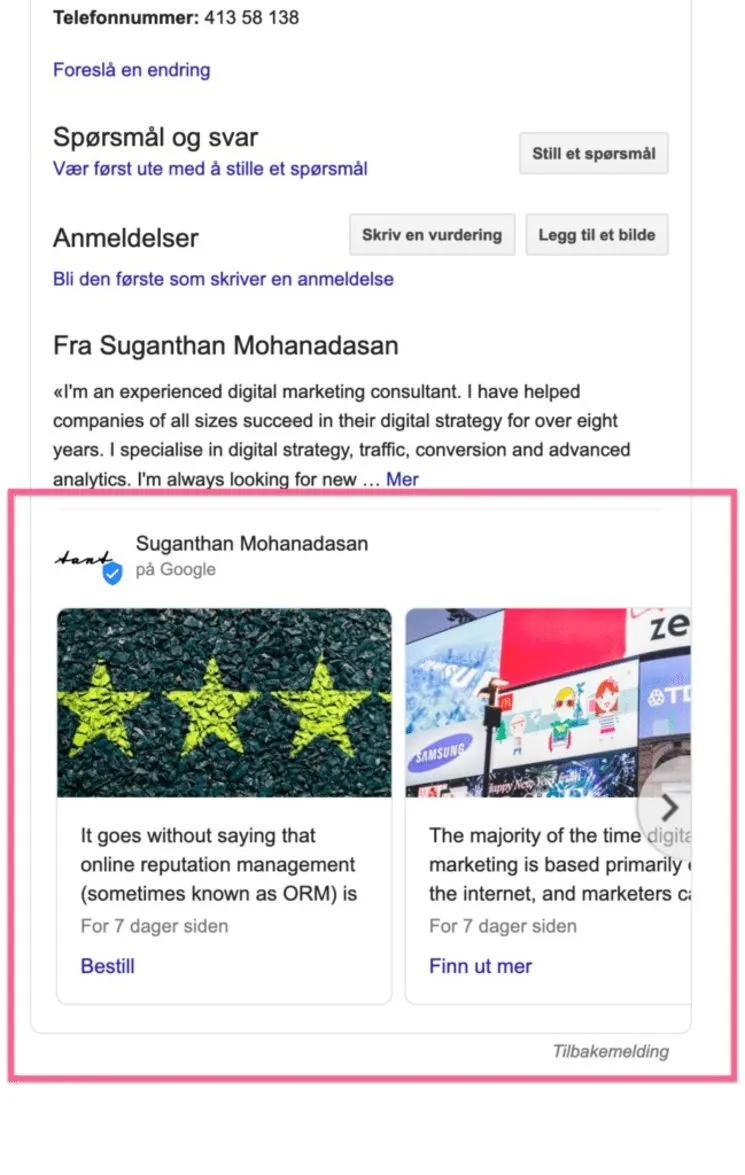
Local search represents approximately 46% of search queries, making local optimisation essential for businesses serving specific geographic areas.
Foundational Elements:
- Accurate NAP information (Name, Address, Phone)
- Google My Business registration
- Bing Places for Business listing
- Local citations and directory listings
- Locally-relevant keyword targeting
- Review management and curation
Advanced Strategies:
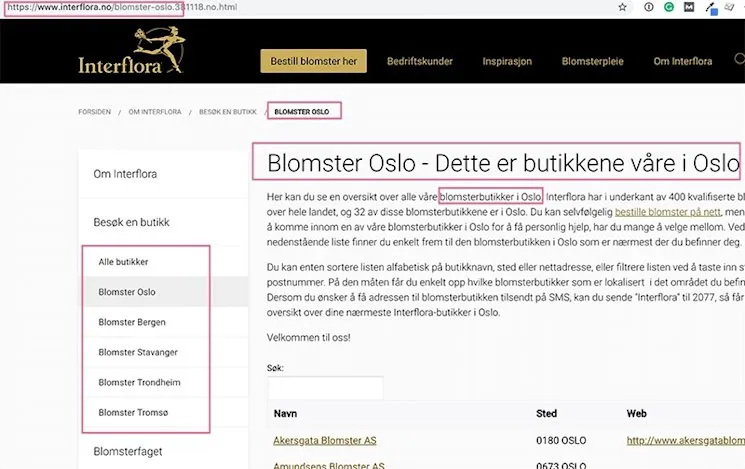
- Creating city-specific landing pages
- Optimising for “near me” and “around me” searches
- Posting regularly to Google Business pages
- Managing multiple location profiles appropriately
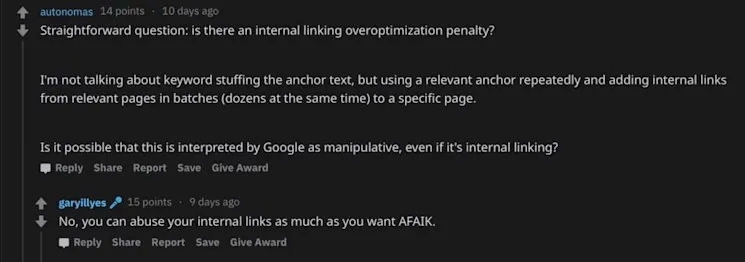
6. Understand Why Internal Linking Is So Important
Internal links facilitate navigation for both users and crawlers, enabling discovery of pages and site areas.
- Ensure homepage reachability from any page within 2-3 clicks
- Link all important landing pages
- Include textual links within blog content to relevant services/products
- Maintain reasonable link quantities per page
Recent confirmation from Google suggests no over-optimisation penalty exists for excessive internal linking, though quality and strategic placement remain important.
7. Investigate Topic Modelling
Modern search algorithms prioritise topic-based content over keyword density. This approach structures content as:
- Pillar page: Comprehensive resource addressing core topic
- Related pages: Detailed explorations of subtopics
- Internal linking: Semantic connections between resources
Benefits include demonstrating topical depth and authority, improving crawler understanding, enhancing user navigation, and boosting pillar page authority and rankings.
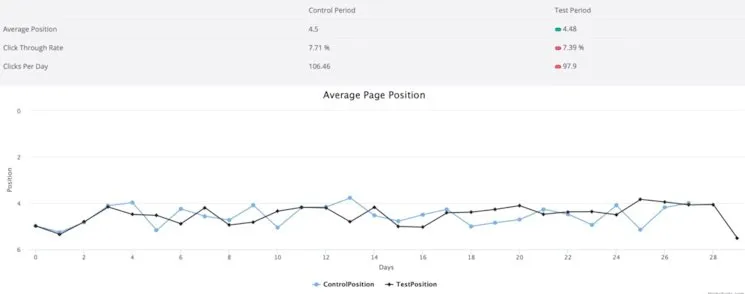
8. Look to Intelligently Raise Your Click-Through Rates
Organic click-through rates (CTRs) significantly impact search visibility and conversion performance.
CTR Optimisation Strategies
- Prioritise quality content over keyword density
- Enhance emotional resonance and relatability
- Use lists, bullet points, and scannable formatting
- Employ powerful language in title tags
- Maintain descriptive, readable URLs
9. Find New Ways of Using the New Google Search Console
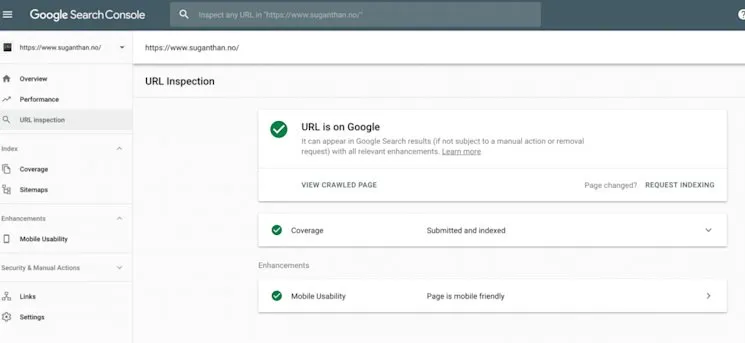
Google’s redesigned Search Console provides enhanced functionality:
- Search Performance data
- Index Coverage analysis
- AMP Status monitoring
- Job Posting validation
- URL Inspection tool with HTTP response codes, page resource analysis, JavaScript console logs, and rendered page screenshots
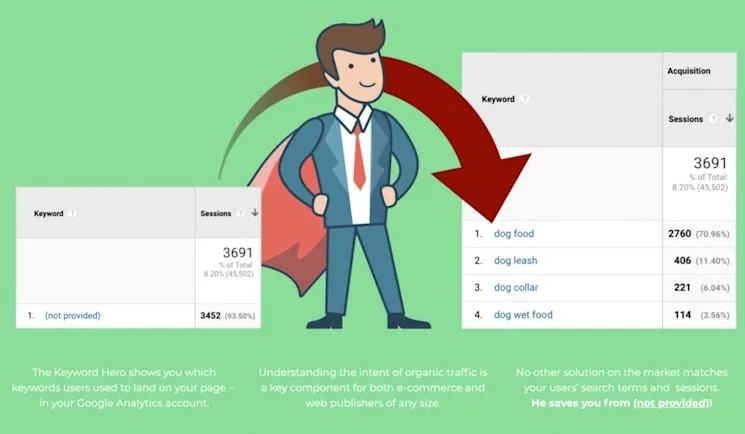
10. Decrypt “not_provided” Organic Keywords in Google Analytics
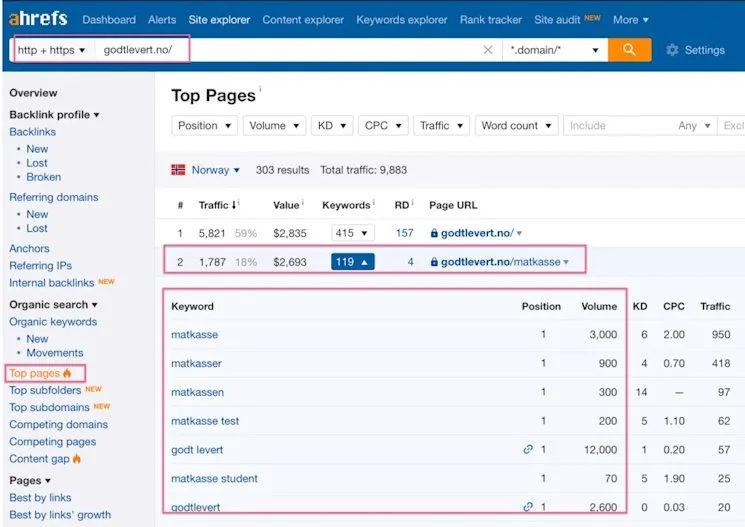
Since 2011, Google encrypted organic search keyword data in Analytics. Alternative approaches include:
- Semrush and Ahrefs provide keyword ranking reports
- Keyword Hero uses machine learning to match Google Search Console queries with Analytics sessions
11. Implement Hreflang for International SEO
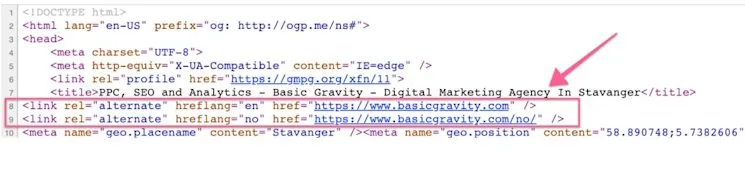
Hreflang HTML attributes signal relationships between pages across languages and regions. Key benefits:
- Eliminates duplicate content concerns for multi-language variants
- Signals Google to maintain regional versions in index
- Directs users to appropriate language/country-targeted pages
- Improves user experience through proper localisation
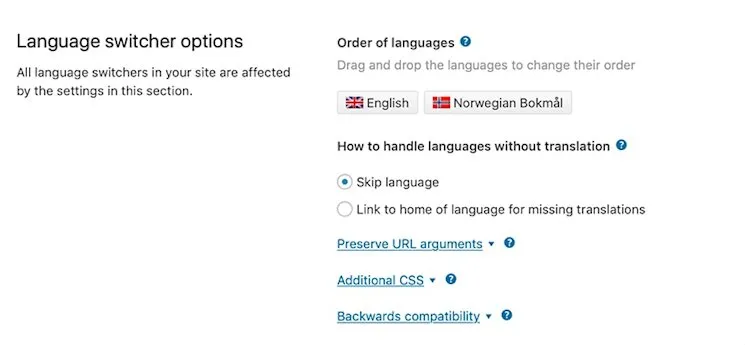

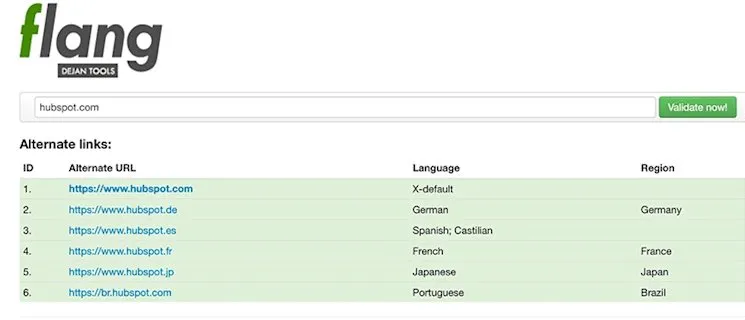
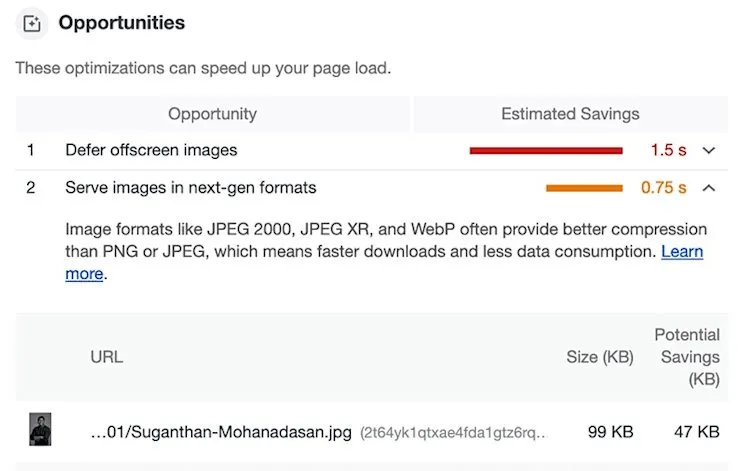
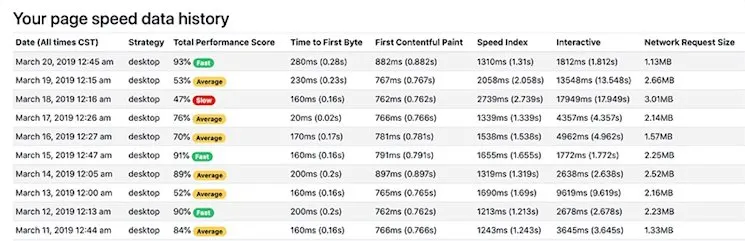
12. Consider Your Page Load Speeds
Mobile search dominance makes page speed critical, especially with Mobile-First Indexing.
Slow loading pages negatively influence:
- Bounce rates
- User experience signals
- Mobile-First Index rankings
- Engagement metrics
Target a reasonable 2-second load time. Use Google PageSpeed Insights for diagnostics.
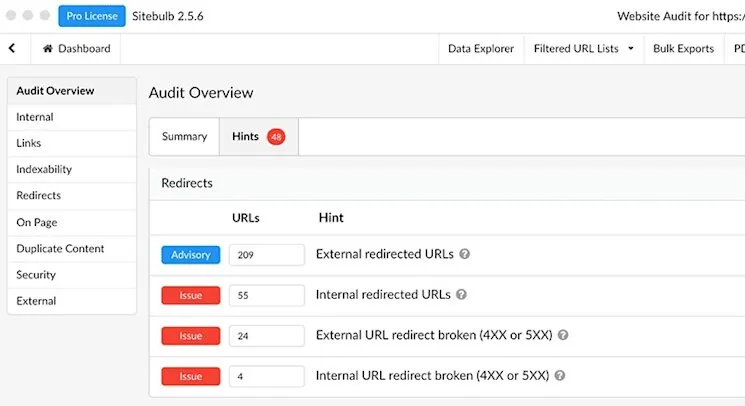
13. Use the Correct Redirects
- 301 Redirects (Permanent): Pass approximately 99% of link equity. Preferred redirect type.
- 302 Redirects (Temporary): Reserve for temporary page unavailability.
- 404 Errors: Indicate non-existent pages without redirects. Require resolution.
Common Redirect Problems
- Redirects pointing to non-existent pages (404s) or redirect chains
- Using 302 instead of 301 for permanent moves
- Internal links pointing to redirected URLs — wastes crawl budget
14. Ensure That Your Site Is on HTTPS
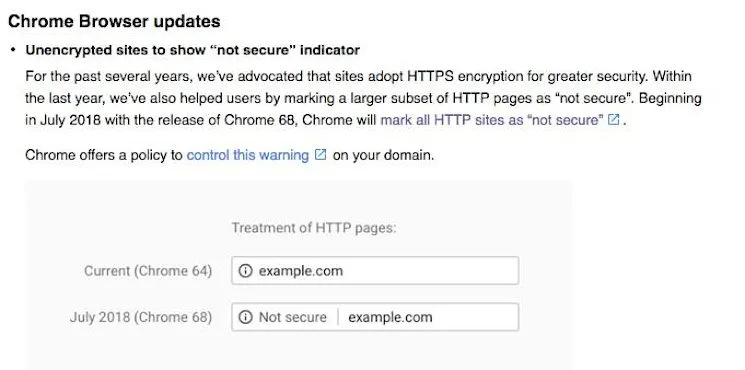
Google prioritises security across all services. Since July 2018, Chrome marks non-HTTPS sites “not secure.” Google has signaled ranking boosts for HTTPS sites.
Free certificates are available via Let’s Encrypt.
15. Optimise Your Site for Mobile
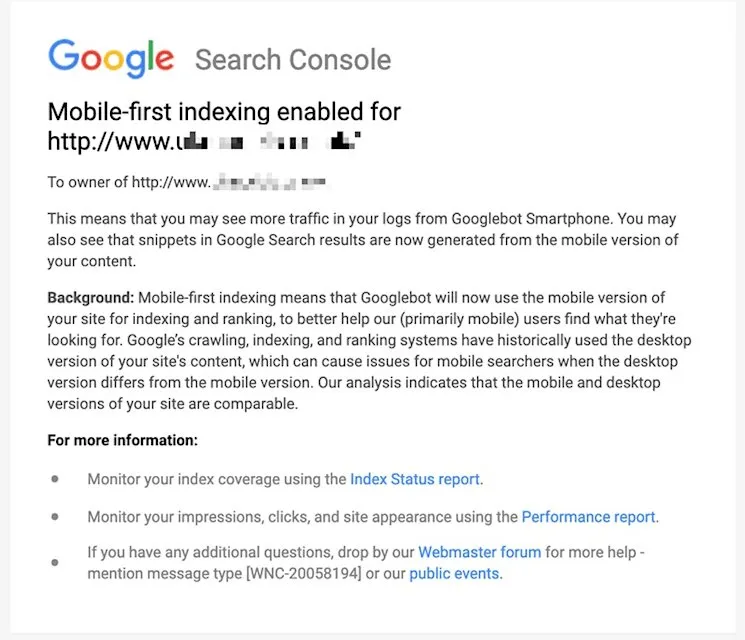
Mobile-First Indexing prioritises mobile site versions for ranking assessment.
Mobile optimisation essentials:
- Responsive design accommodating various devices
- XML and media sitemap optimisation
- Meta description and media optimisation
- Structured data implementation
- AMP consideration
16. Optimise Your Site for Voice Search
Voice search adoption continues accelerating through Siri, Cortana, Google Now, Alexa, and Google Assistant.
Voice Search Characteristics
- Longer, conversational queries
- 22% include local search intent
- Increasing “near me” searches
- Information-focused rather than transactional (currently)
Voice Optimisation Strategies
- Create comprehensive FAQ pages
- Incorporate conversational, long-tail keywords
- Implement structured data markup
- Focus on Featured Snippet optimisation (primary Google Assistant source)
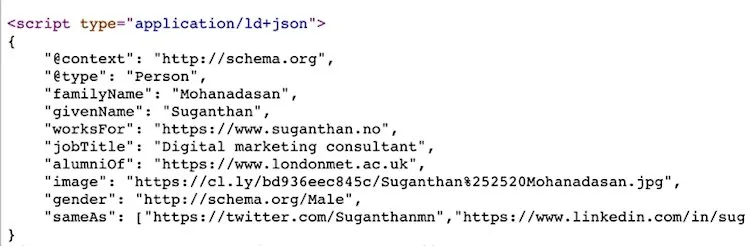
17. Don’t Overlook Schema.org Markup
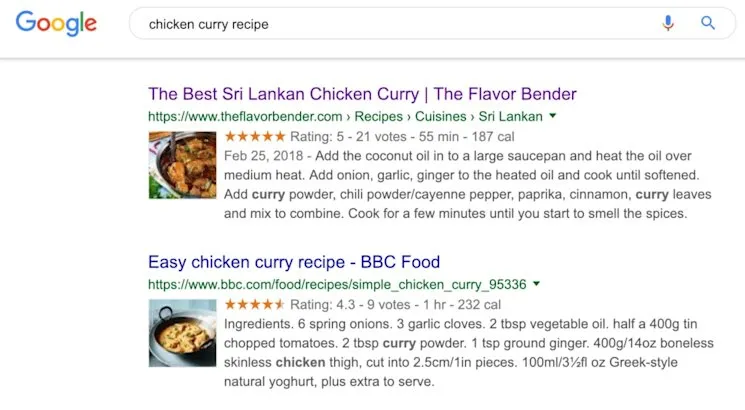
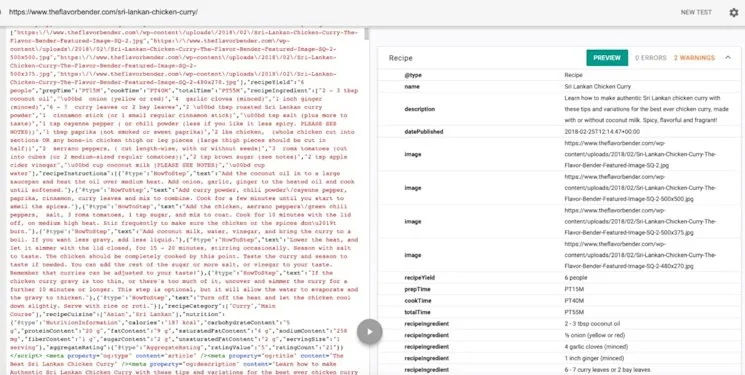
Schema.org markup provides HTML tags signalling crawler interpretation guidance for SERP representation. Google prefers JSON-LD schema markup.
Structured data enables rich SERP features including:
- Star ratings and review counts
- Product pricing and availability
- Event details and dates
- Recipe instructions with ratings
- FAQ structured answers
Key markup types to consider: creative works, events, organisations, people, places, and products.
18. Utilise Social Media to Your Advantage
While Google remains ambiguous about direct social signal ranking impacts, social media channels offer indirect SEO benefits:
- Social profiles rank in search results
- Active profiles drive platform-specific discovery
- Social sharing accelerates indexing
- Twitter sharing is particularly effective for rapid link discovery
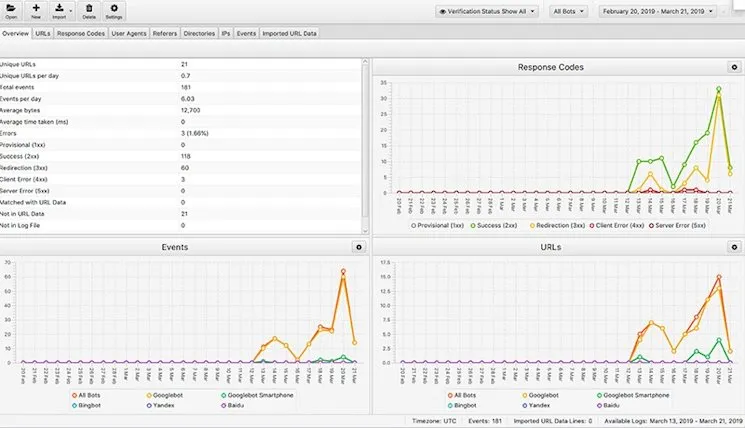
19. Bonus Tip: Log File Analysis
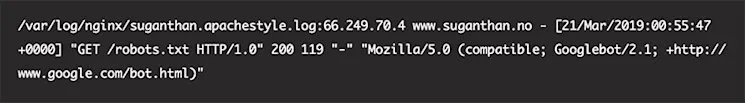
Log file analysis examines server records documenting visitor and crawler behaviour, providing insights into Google bot activity.
Analysis reveals:
- Google bot crawler types and frequencies
- Top crawled folders and pages
- Crawl patterns and priorities
- Server response codes
- Crawl efficiency and budget usage
Log Analysis Tools:
- Screaming Frog Log Analyzer (paid)
- Seolyzer (free)
- Log Hero (integrates with Google Analytics)
You might also like
Stay in the loop
I'll email you when I publish something new. No spam. No fluff.
Join other readers. Unsubscribe anytime.

Entrepreneur & Search Journey Optimisation Consultant. Co-founder of Keyword Insights and Snippet Digital.