What Will It Mean to Do SEO in 2020 and Beyond?
Exploring the evolution of SEO as search engines become smarter and user behaviour shifts across platforms.
Note: This article was originally published on the Moz blog, but it has since been removed, likely due to its age. A preserved copy is available via the Internet Archive here
Without a doubt, it is our job as SEOs to keep an eye on the future and anticipate what Google is planning, testing, or looking to drop on our doorsteps. Over the past 12 months alone, we have seen several changes in Google Search — each impacting how we plan, implement, and report on campaigns.
In this article, I will take a look at what is in store for SEO in 2020 and how these factors will change the way we formulate strategies throughout the next year and beyond.
Artificial intelligence will continue to evolve
Over the past half-decade, artificial intelligence has become a pioneering force in the evolution of SEO.
In 2015, for example, we were introduced to RankBrain — the machine-based search algorithm that helps Google push more relevant results to users. Although RankBrain is coming up on its fifth birthday, we are only now catching early glimpses into how artificial intelligence will dominate SEO in the coming years.
The most recent step in this progression of artificial learning is, of course, the introduction of Bidirectional Transformers for Language Understanding (BERT), which Google announced at the end of October . For those who missed it, BERT is Google’s neural network-based technique for natural language processing, and it’s important because it deals with the very fundamentals of how people search. Google itself says that the algorithm represents “the biggest leap forward in the past five years, and one of the biggest leaps forward in the history of Search.”
Affecting one in ten searches, BERT gives Google a better understanding of how language is used and helps it comprehend the context of individual words within searches. The important thing to know about BERT (and also RankBrain), is the fact that you cannot optimize for it.
But what does this mean for SEOs?
BERT is just one signal of how Google understands language, but it is one of the most important in the search engine’s arsenal. This means that now more than ever, webmasters and SEOs alike must focus their efforts on creating the most useful, natural, and highest-quality content. Quite simply, as Danny Sullivan says, “write content for users.”
It’s also worth understanding how BERT interprets questions, which you can find out more about in the Whiteboard Friday episode below.
Voice search is here to stay
It’s hard to imagine at the dawn of 2020, but when voice search was released in 2012 many assumed it would be just another project consigned to the ever-growing Google graveyard .
Today, however, we know so much more about the technology and, thanks to schema.org, where it is likely to go in the future. The adoption rate is slower than predicted, but it has nevertheless leaked into our lives, so we must not completely ignore voice search.
Schema markup
A new form of markup is released nearly every month, with one of the latest developments being markup for movies . Although this might seem insignificant, the fact that we are now seeing markup for films shows just how granular and far-reaching structured data has come.
With smart speakers now numbering 120 million in the US alone, webmasters should be taking the time to investigate where schema can be placed on their website so they can take advantage of the 35.6 million voice search demands taking place every month. What’s more, website markup has a monumental influence on featured snippets, which can be highly lucrative for any website. Take a look at this Moz guide for more information on how voice search influences featured snippets .
Speakable
If you’re in the US, it’s also worth noting that Speakable (BETA) is used by Google Assistant to answer people’s questions about specific topics. The assistant can return up to three relevant articles and provide audio playback using text-to-speech markup. Implementing such a markup can be highly lucrative for news sites, because when the assistant provides an answer, it also attributes the source and sends the full article URL to the user’s mobile device. If you’re a news site that publishes in English but doesn’t yet have Speakable markup implemented, you can read up on both the technical considerations and content requirements necessary for eligibility.
Google Actions
Actions on Google , a development platform for Google Assistant, is also worth your consideration. It allows the third-party development of “actions” — applets for Google Assistant that provide extended functionality. Actions can be used to get things done by integrating your content and services with the Google Assistant.
Actions allow you to do a number of things:
- Build Actions to ensure Google Assistant uses your apps
- Allow users to search for and engage with your app
- Provide your app as a recommendation for user queries
Check out this fantastic article by Andrea Vopini about how to optimize your content using Google assistant.
Google is heavily invested in using entities
Entities aren’t something that you hear SEOs talking about every day, but they are something Google is putting a lot of resources into. Put simply, Google itself states that entities are “a thing or concept that is singular, unique, well-defined, and distinguishable.”
Entities don’t have to be something physical, but can be something as vague as an idea or a color. As long as it is either singular, unique, distinguishable, or well-defined, it is an entity.
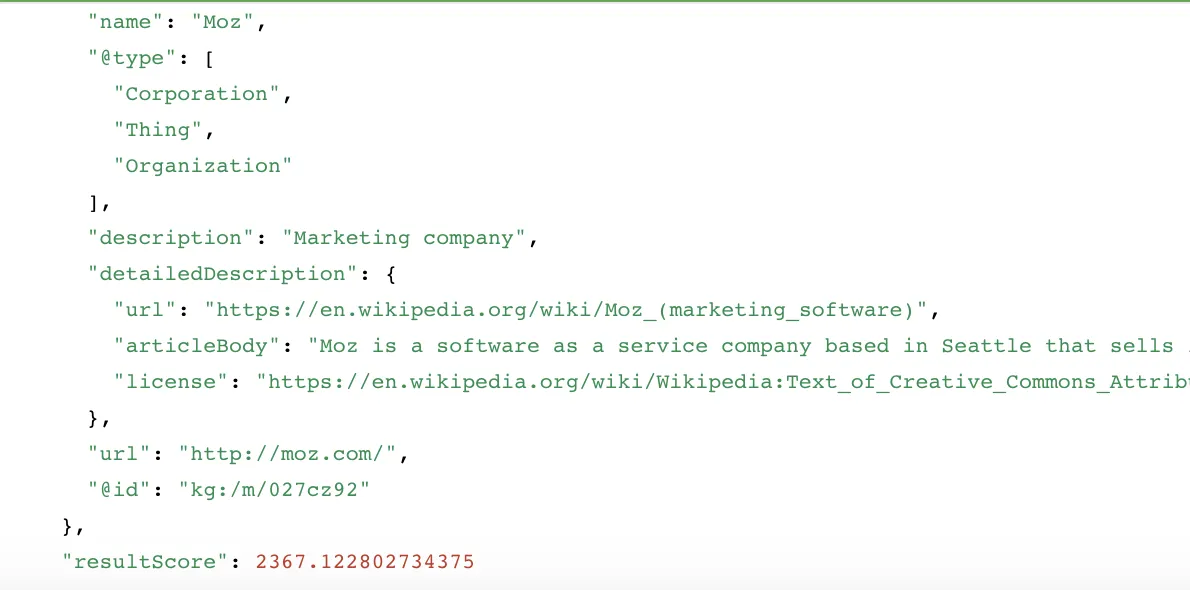
.DqfdOHO9_2GUhi.webp)
As you can see, Moz shows up in the knowledge panel because the company is an entity. If you search the Google Knowledge Graph API for the company name, you can see how Google understands them:
But what does this mean for SEOs?
In 2015, Google submitted a patent named “ Ranking Search Results Based On Entity Metrics ,” which is where the above entity description is sourced from. Although few patents are worth getting excited about, this one caused a stir in the technical SEO scene because it takes machine learning to an entirely new level and allows Google to accurately calculate the probability of user intent, thus giving it an understanding of both user language and tone. What’s more, entities place a reduced reliance on links as a ranking factor, and depending on what your SEO strategy is, that could result in the need for big campaign changes.
The most important aspect you will need to consider is how Google understands the entities on your website.
For example, if your site sells shoes, you need to think about how many different types, colors, sizes, brands, and concepts exist for your shoes. Each shoe will represent a different entity, which means you must consider how to frame each product so that it meets the expectations of users as well as the learning capabilities of Google — which is where we meet markup once again .
Sites themselves can also become entities, and that provides huge rewards as they appear in the Knowledge Panel, which I will discuss next.
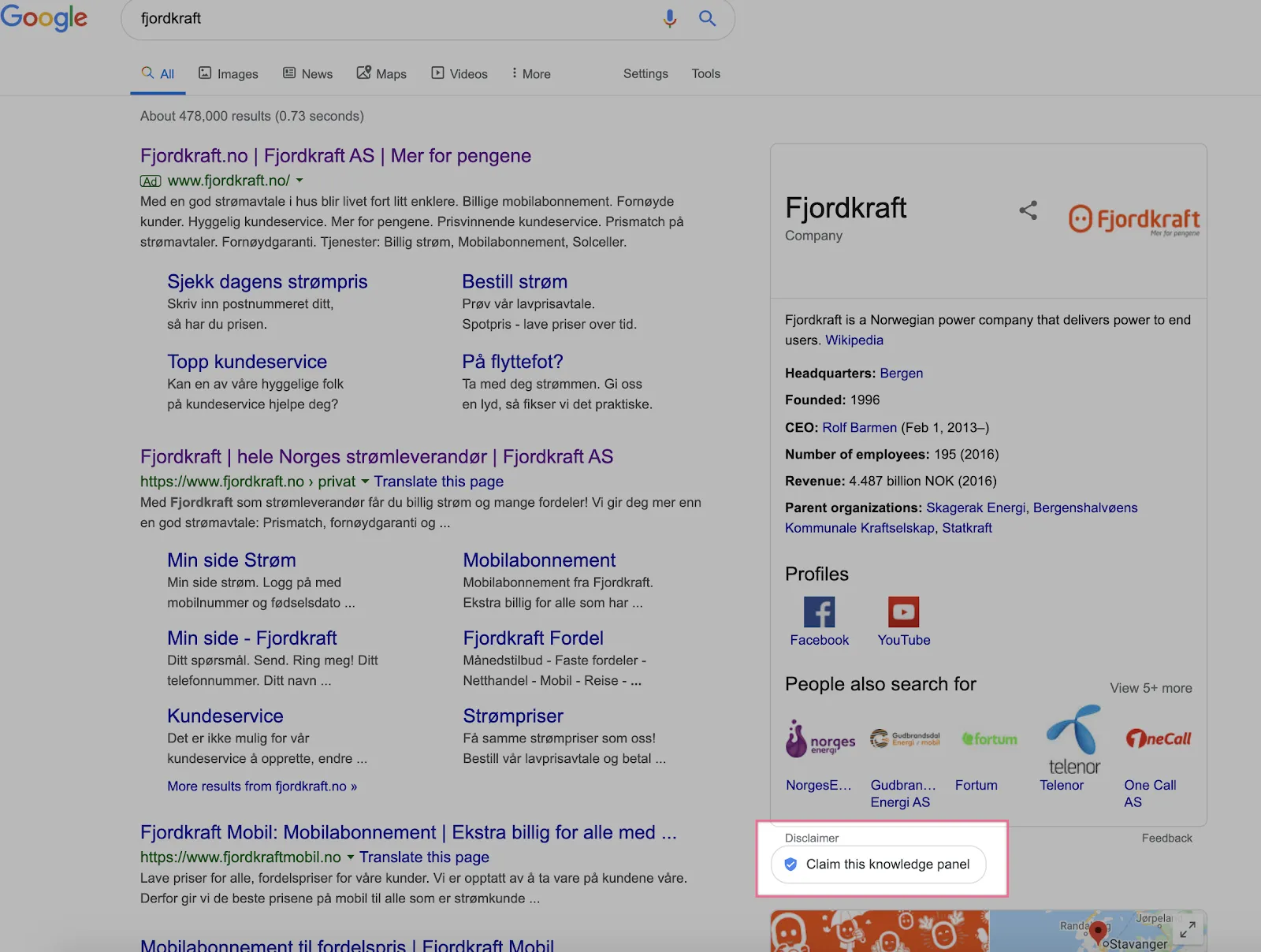
The knowledge panel will be important for personalities and brands
Although Google’s Knowledge Graph was launched way back in 2012, its expansion since then means it is still a core part of the search matrix and one that will reach far into the next decade.
Closely tied with featured snippets and rich results, earlier last year Google began allowing entities to claim their own knowledge panel, giving them access to edit and control the information presented to users in search results. They can make specific requests, such as changing the featured image, panel title, and social profiles provided within the panel.
The benefits of claiming your knowledge panel are numerous. They help users gain quick access to your site, which thanks to the Knowledge Graph, displays trust and authority signals. Knowledge panels also provide brands and personalities with the ability to control what objective information is shown to users. However, there are still many brands that have yet to claim their own panels.
You can claim your business’s knowledge panel in a few easy steps:
- Ensure that your website is verified with Search Console .
- Update your panel by suggesting a change to Google.
But what does this mean for SEOs?
As you can see from the above examples, being in the Knowledge Graph can improve trust and add authenticity to your business or personal brand, as well as providing additional visibility. But it’s easier said than done.
Unless you’re a recognized, famous person or brand, claiming space in the Knowledge Graph is going to be difficult. Having a Wikipedia page can be enough, but I don’t recommend creating pages just to get there — it will get deleted and waste your effort. Instead, build brand mentions and authority around your name gradually. While having a wikidata page can be helpful, it’s not guaranteed. The goal is to get Google to recognize you as a notable person or brand.
Queryless proactive predictive search is getting better
Google Discover was released in June of 2017, prompting a new kind of search altogether — one that is queryless. Discover is an AI-driven content recommendation tool and claims 80 million active users.
Using the aforementioned Knowledge Graph, Google added an extra layer called the Topic Layer, which is engineered to understand how a user’s interest develops over time ( this article by the University of Maryland offers an in-depth explanation of topic layers and models).
By understanding the many topics a user is interested in, Discover identifies the most accurate content to deliver from an array of websites.
But what does this mean for SEOs?
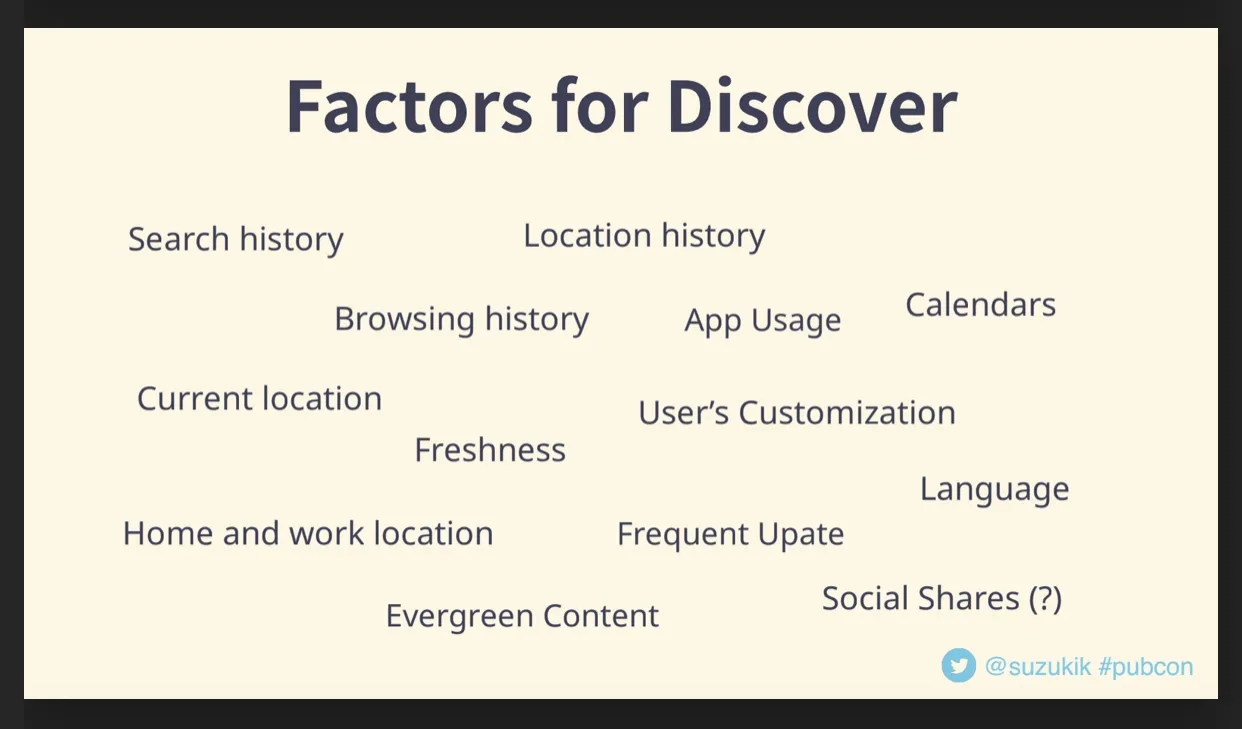
To appear in Discover, Google states that pages appear “if they are indexed by Google and meet Google News content policies . No special tags or structured data are required.” It ranks content based on an algorithm that inspects the quality of content alongside the interests of the user and the topic of the page in question. The exact formula is unknown, however, based on several studies and experiments we now have a pretty good idea of how it works.
This screenshot from a presentation by Kenichi Suzuki highlights some of the factors that help pages appear in Discover.
According to Google , there are two ways to boost the performance of your content within Discover:
- Post interesting content
- Use high-quality images
As ever, ensure that you generate high quality content that is unique and creates a great experience for users. If your site tends to publish clickbait articles, the chance of those articles appearing in Discover is low.
Other tips for appearing in Discover would be to arrange your content semantically so that Google finds it easier to understand your work, and ensure that your website is technically proficient.
Like any form of search, you can use Google Search Console to see how well your articles are performing in Discover. You can find Discover stats under the performance section.
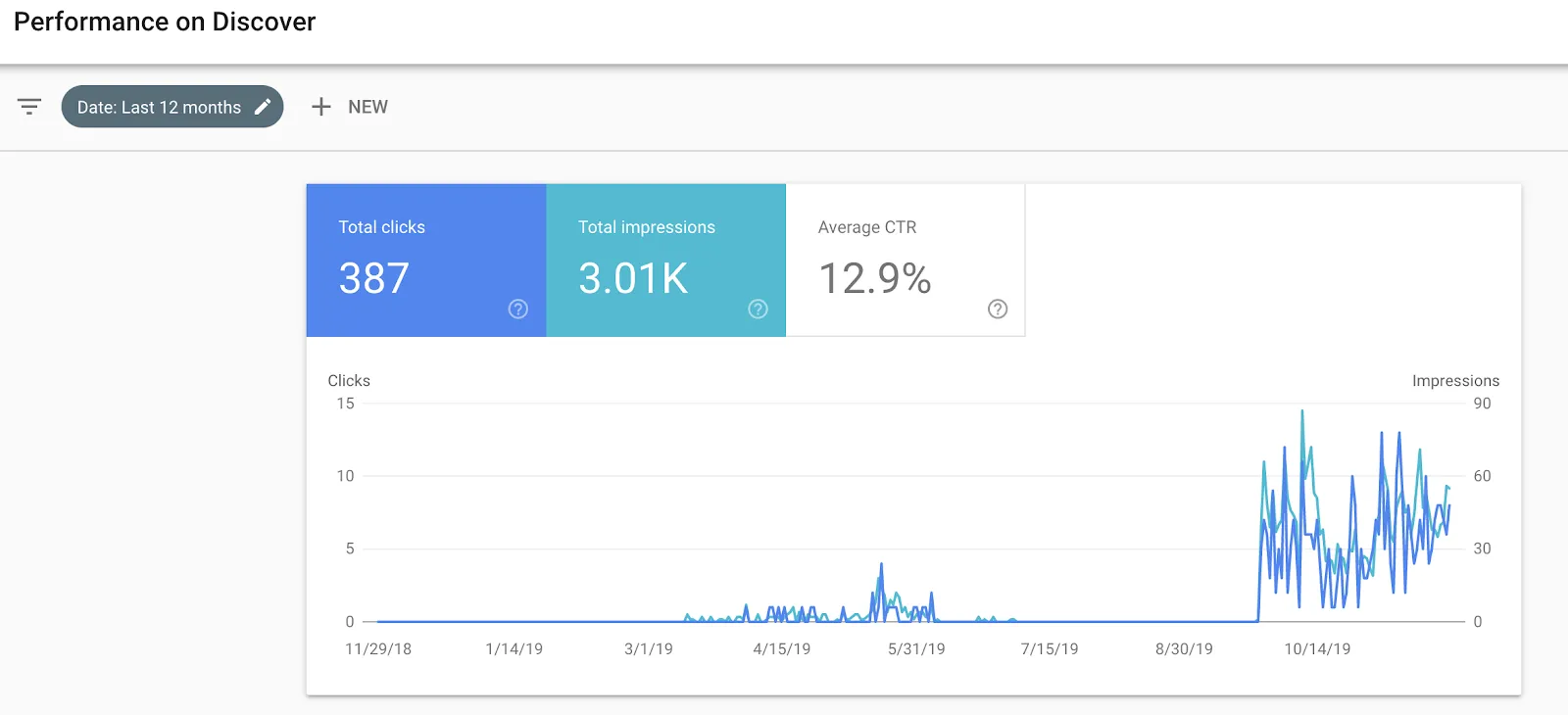
Google Discover analytics data is fairly new, and therefore limited. There isn’t currently a native way to segment this traffic inside Google Analytics. To track user behavior data, this article provides a technique to track it inside Google Analytics.
We have yet to see the biggest changes in visual image Search
It could be argued that the biggest change to image search happened in September 2018 when Google Lens rolled out. Not only did featured videos begin appearing in image search, but AMP stories and new ranking algorithms and tags were also released.
But while speaking at a Webmaster Meetup in New York last year, John Mueller shared that there will be major changes in image search in the coming year. Rather than merely viewing images, very soon people will use itto accomplish goals, purchase products, and learn new information.
Google has always said that images should be properly optimized and marked, so if you have not started to add such data or information to your images, now is definitely the time to start.
In the past six months alone we have seen Google introduce small changes such as removing the “view image” function, as well as colossal changes, such as totally revamping image search for Desktop .
Furthermore, people don’t even have to search within it to see images anymore. It’s common for the SERP to present a universal search result, which encompasses images, videos, maps, news, and shopping listings. The opportunity to appear in a universal (or blended) result is just another reason why properly tagged and marked images are so important.
Finally, Google has added visual image search attributes to search results. The interesting thing with this update is that these attributes are now available as image carousels within the main search results.
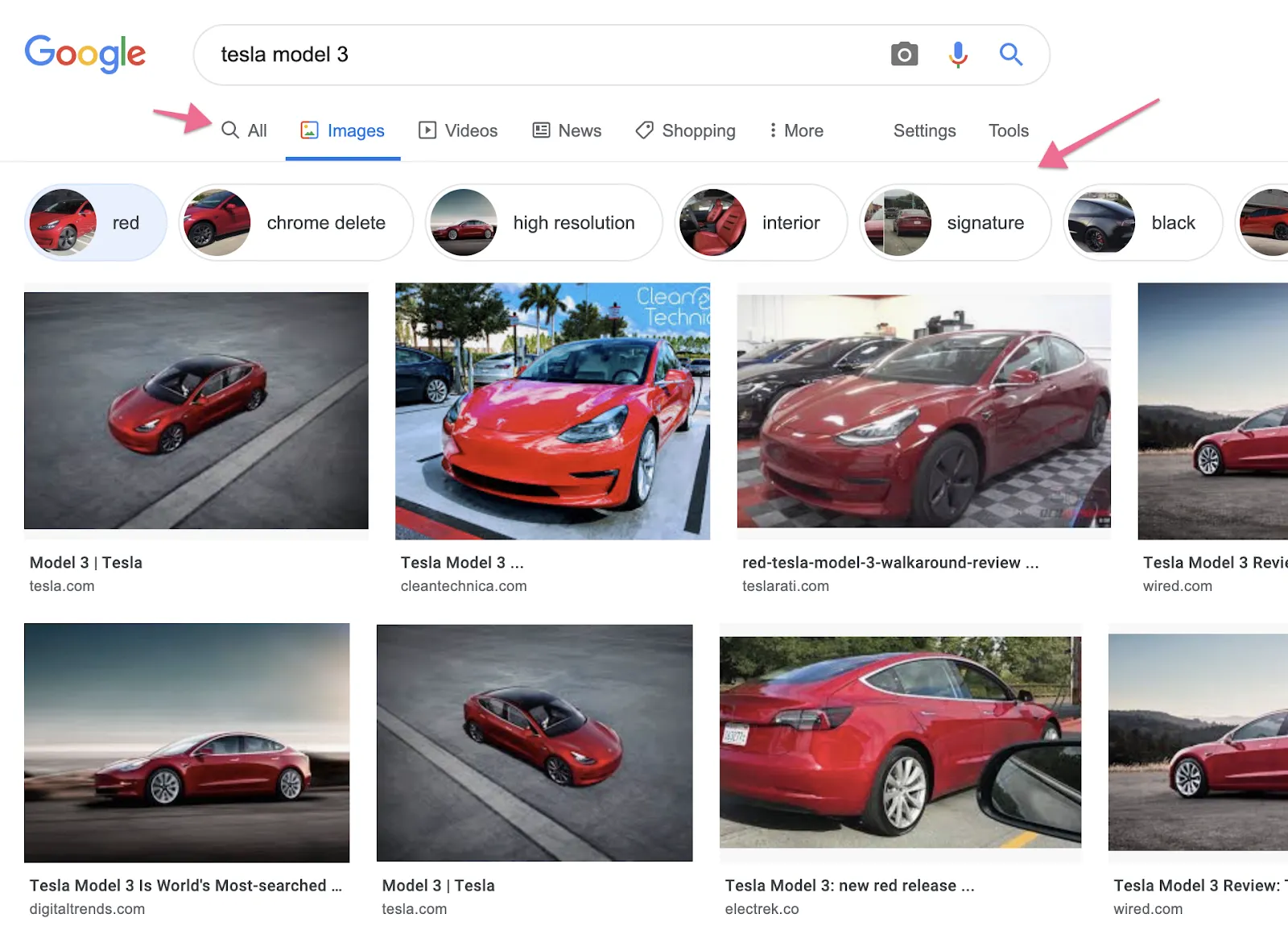
But what does this mean for SEOs?
With so much to play with, webmasters and SEOs should consider how they can take advantage of such changes, which could prove potentially very lucrative for the right sites — especially when you consider that 35% of Google product searches return transactions in as little as five days.
E-A-T doesn’t apply to every site — but it still matters
E-A-T (Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness) is something every SEO should know back to front, but remember:
- E-A-T isn’t a ranking factor
- E-A-T is critical for Your Money or Your Life (YMYL) topics and pages
Although these two statements might seem contradictory, they make more sense when you consider what Google defines as YMYL.
According to Google’s Rater Guidelines , YMYL is a page or topic that “could potentially impact a person’s future happiness, health, financial stability, or safety.” This means that if your page has information that could potentially change a person’s life, it is considered YMYL and offering E-A-T is important. If your site is merely your personal collection of cat pictures, then showcasing authority or expertise is less critical.
But what does this mean for SEOs?
The issue, however, is that the majority of websites (and certainly the ones invested in SEO) are generally going to have YMYL pages or topics, but Google is taking big steps to ensure that low quality or questionable YMYL content is weeded out. As you might know, you can’t optimize for E-A-T because it isn’t an algorithm, but you can implement changes to make sure your site sends the right kind of quality signals to Google. This Moz article by Ian Booth and this guide by Lily Ray offer great tips for how to do that.
Topics and semantics over keywords
Google is putting less priority on both links and keywords, which is where topic modeling and semantics come into the conversation.
Google has become very clever at understanding what a user is searching for based on just a few basic words. This is thanks, in part, to topic modeling (as Google itself admitted in September 2018 when it introduced its “topic layer” ). Indeed, this algorithm has a deep understanding of semantics and yearns to provide users with deep troves of information.
But what does this mean for SEOs?
This means that it has never been more important to create high quality, in-depth, and meaningful content for users — but you also need to think about information structure.
For example, if your site sells running shoes, you could create long-form educational pieces about how to choose shoes for specific running environments, athletic diets for runners, or tech accessory reviews. These articles could then be clustered into various topics. By clustering your topics into compartments through your website architecture, both users and crawlers can easily navigate and understand the content provided.
Studies have also shown that Google’s crawlers prefer pages with semantic groupings and sites that are designed around topic modeling. This 2018 presentation by Dawn Anderson gives a brilliant insight into this. If you want to know more about topic modeling and semantic connectivity, check out this Whiteboard Friday by Rand Fishkin.
SERPs will continue to evolve
Over the past couple of years, we’ve seen search results evolve and transform like never before. In fact, they have changed so much that, in some cases, being placed first within the organic search results may not be the most lucrative position.
This is something that would have been unthinkable just a few short years ago ( check out this Moz article from 2018 ) that works to quell the panic from zero position SERPs).
With the introduction of Voice Search, rich results, rich snippets, knowledge panels, Google My Business, and updated Image Search results, SEOs now need to consider a whole new range of technical marketing strategies to appear in a multitude of organic search results.
It’s hard to know where Google is taking SERPs in the next year, but it is fair to say the strategies we use today for the search environment will likely be outdated in as little as six months.
Take, for example, the recent addition and subsequent removal of favicons in the SERPs; after backlash, Google reversed the change, proving we can never predict which changes will stick and which are blips on the radar.
But what does this mean for SEOs?
Ensure that your strategies are flexible and constantly prepare for changes in both your business sector (if you do not work within SEO) and the constantly evolving search environment. Pay attention to the seasonality of searches and use tools such as Google Trends to cover any out-of-season deficit that you may encounter.
You can use tools like Moz Keyword Explorer to help plan ahead and to create campaigns and strategies that provide useful traffic and lucrative conversions.
Final Thoughts
SEOs need to move away from the ideology that links and traditional search results should be priorities for an organic campaign. Although both still carry weight, without investment in technical strategy or willingness to learn about entities or semantic connectivity, no SEO campaign can reach its full potential.
The world of SEO in 2020 is bright and exciting, but it will require more investment and intelligent strategy than ever before.
You might also like
Stay in the loop
I'll email you when I publish something new. No spam. No fluff.
Join other readers. Unsubscribe anytime.

Entrepreneur & Search Journey Optimisation Consultant. Co-founder of Keyword Insights and Snippet Digital.